ENJOY NATURE IN ROQUETAS DE MAR
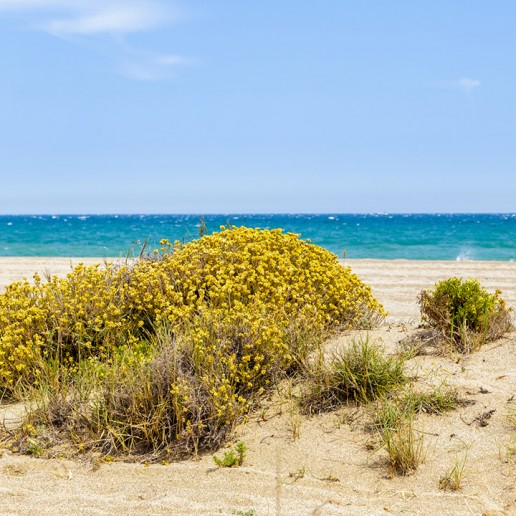
Punta Entinas – Sabinar Natural Park.

The local road of Roquetas de Mar to Punta Entinas-Sabinar leads to a space in which the aesthetic values of the marshes and the Mediterranean scrub are miraculously maintained. Through the beach, consisting of sand and gravel, we access a string of coastal dunes that reach up to seven meters high. The dune strip serves to support the Mediterranean scrub vegetation of large size. Mastics or “entinas” species and junipers live here and they provide refuge for other species of flora and a vertebrate community which is characteristic of semiarid Mediterranean ecosystem. Behind the dunes we can find clay plains with halophytic vegetation.
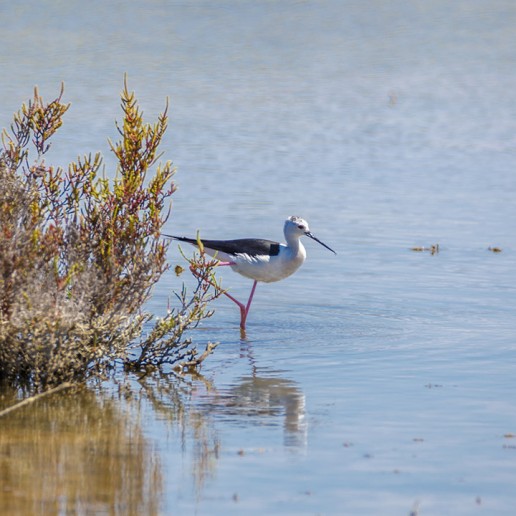
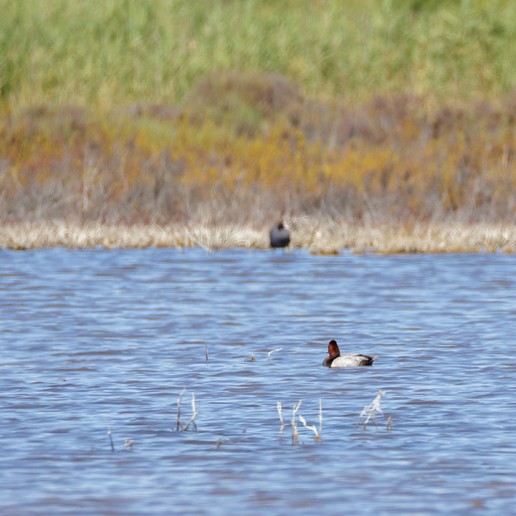
The faunal importance of the area is also marked by the presence of different habitats, the abundance of waterfowl found in the marshes of Punta Entinas-Sabinar which is a mandatory stop in their migrations. In autumn it is easy to see flamingos, egrets and bitterns steppe species like stone curlews or plovers in the ponds near the salt area of Cerrillos and in the lagoons of Punta Entinas.
Besides enjoying the environment around us, this area of Roquetas de Mar has pristine beaches where it is still possible to experience the contact with nature in full freedom, and plenty of paths where cycling or hiking.
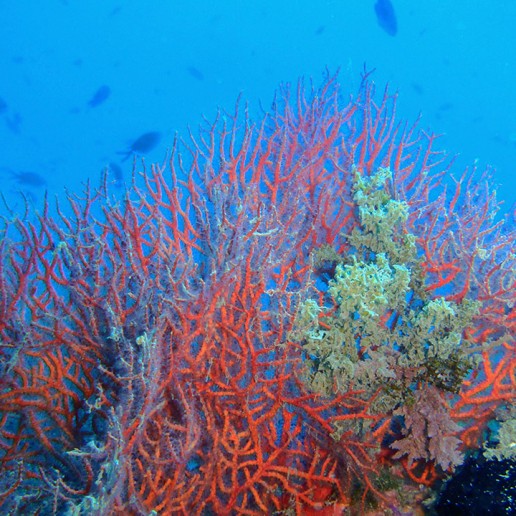
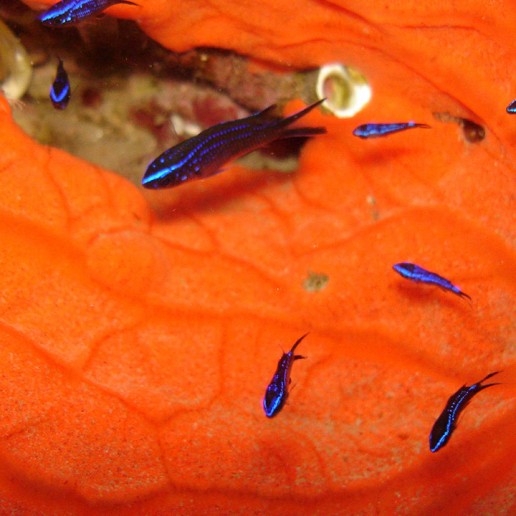
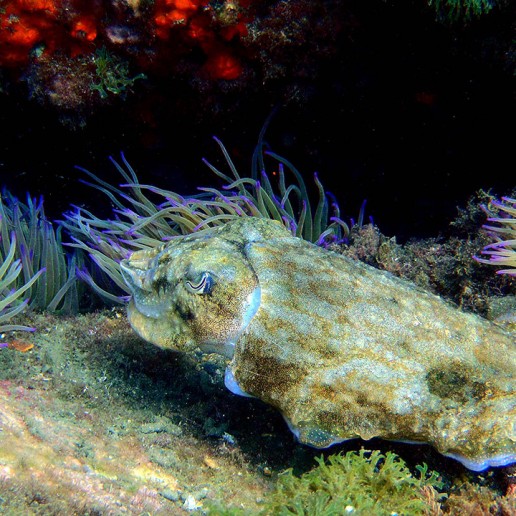
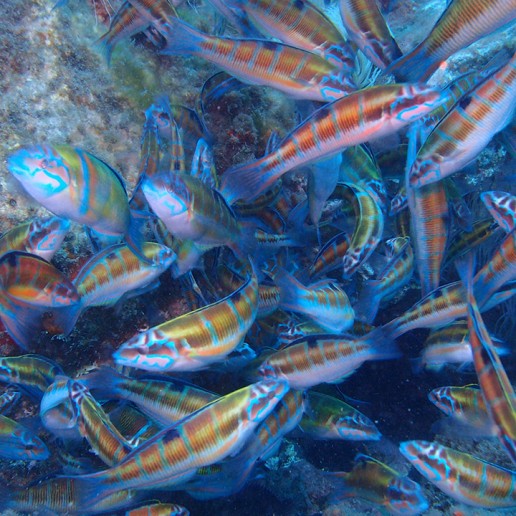
Seabed.

Contemplating life under the sea is one of the most attractive experiences that can be enjoyed on the coast of Roquetas de Mar, due to the richness and diversity of its seabed. Barracudas banks, sea eagles, groupers, moray eels and wrecks are some of the wonders that can be found under the sea, both when practicing snorkeling or diving sports.
In addition, on the beach of Cerrillos, which corresponds to Punta Entinas-Sabinar Natural Park you can enjoy the lushest Posidonia meadow of Roquetas de Mar.
The oceanic Posidonia is a plant with leaves, flowers and fruits, like those we find in forests and gardens, but lives at sea, under water between the surface and 50 meters deep, where there is still light that allows you to develop photosynthesis. Endemic to the Mediterranean Sea, Posidonia form the climax ecosystem most important of the Mediterranean Sea, equivalent to forests in terrestrial ecosystems.
The oceanic Posidonia is a plant with leaves, flowers and fruits, similar to those we find in forests and gardens, but lives at sea, under water between the surface and 50 meters deep, where there is still light that allows it to develop photosynthesis. Endemic to the Mediterranean Sea, Posidonia meadows form the most important climax ecosystem of the Mediterranean Sea, equivalent to forests in terrestrial ecosystems.